Hyperledger Fabric Intro
Hyperledger Fabric
Hyperledger Fabric 1.4 LTS - long-term support release
Hyperledger Fabric is a permissioned blockchain network(许可区块链网络).
Hyperledger Fabric Architecture
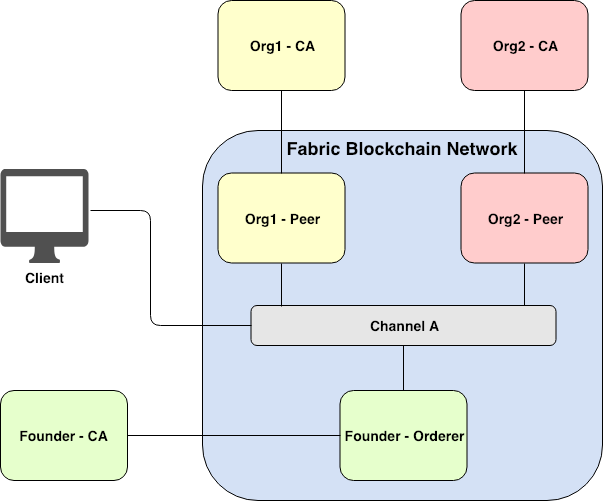
- Simplest Hyperledger Fabric network with two organizations joining the same channel
1 | # Fabric components |
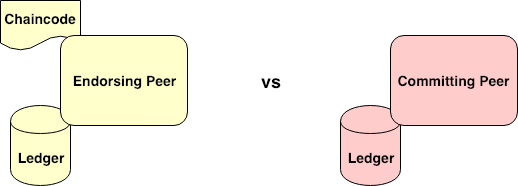
Endorsing Peer(背书) vs Committing Peer()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11# Chaincode (Smart Contract)
- three language (Golang, Nodejs, Java) program Fabric chaincode - 链码
- 要部署链码,网络管理员将链码安装到目标peer,然后调用orderer排序节点将链码实例化到特定channel通道上.
- Endorsement policy defines which peers need to agree on the results of a transaction before the transaction can be added onto ledgers of all peers on the channel.
- A chaincode developer must opt to use either LevelDB or CouchDB when developing a chaincode.
# Endorsing Peer 背书节点
> which consists of an installed chaincode and a local ledger on it
# Committing Peer
> would have only a local ledger on it.Interior components inside the Peer’s ledger
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
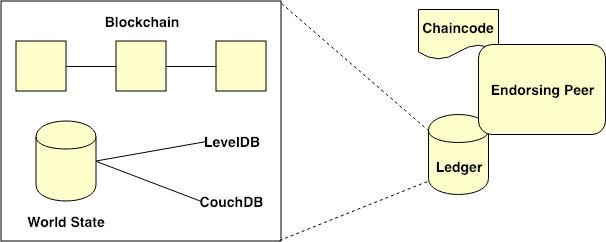
12# Blockchain
> the history of alll transactions for every chaincode on a particular channel.
# World State:
> maintains the current state of variables for each specific chaincode.
- Two type database:
- LevelDB:
> key-value database built on Fabric Peer
- CouchDB:
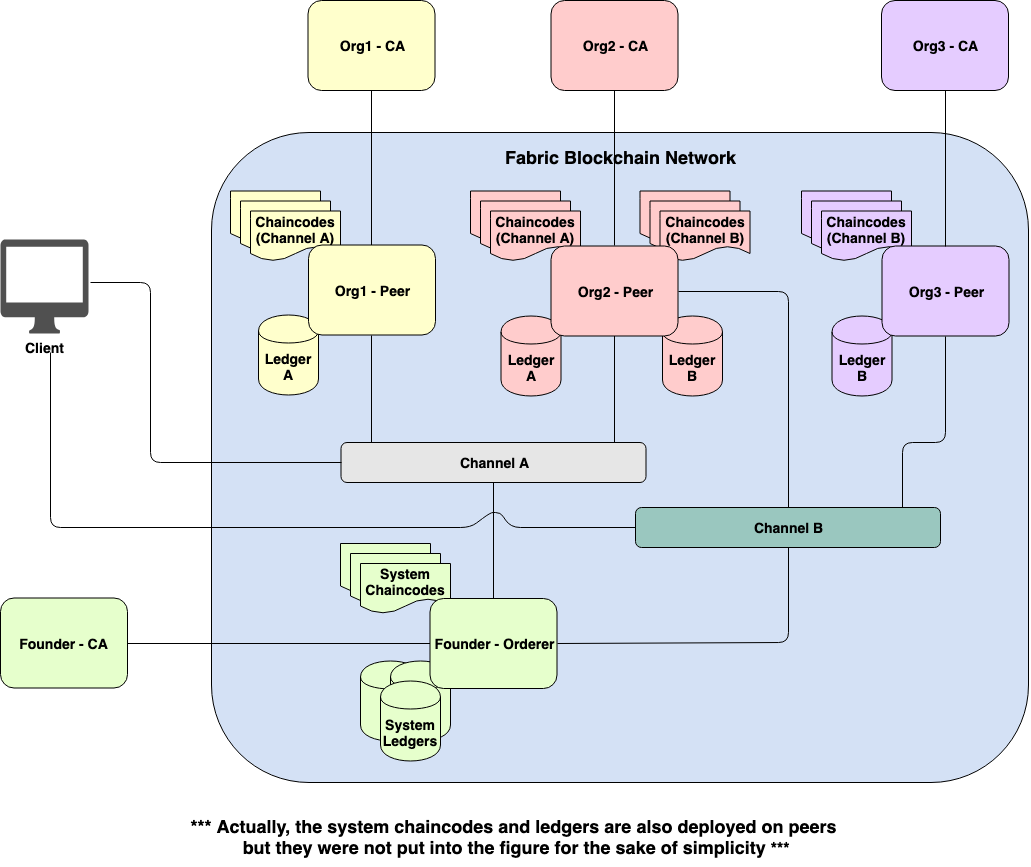
> JSON-based database supporting rich querying operations based on JSON objects.Fabric network with chaincodes and ledgers attached multiple channels
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18> Actually, the system chaincodes and ledgers are also deployed on peers
# System Chaincodes
> collect network, channel, and underlying system configurations for Fabric virtual machine to work properly.
- QSCC (Query System Chaincode): for ledger and Fabric-related queries
- CSCC (Configuration System Chaincode): which helps regulate access control
- LSCC (Lifecycle System Chaincode): which defines the rules for the channel
- ESCC (Endorsement System Chaincode): endorsing transactions
- VSCC (Validation System Chaincode): validating transactions
# System Ledgers
# Channel
> organizations that join the same channel can secretly share business transaction or information together with confidence.
# Chaincode:
- one chaincode can call another chaincode on the same channel.Fabric transaction invocation workflow (投票流程图)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13# consensus(共识) divided into tree phases
- 1. Endorsement (背书) (Steps 1-3)
- 2. Ordering (排序) (Steps 4-5)
- 3. Validation and Commitment(验证和承诺) (Steps 6)
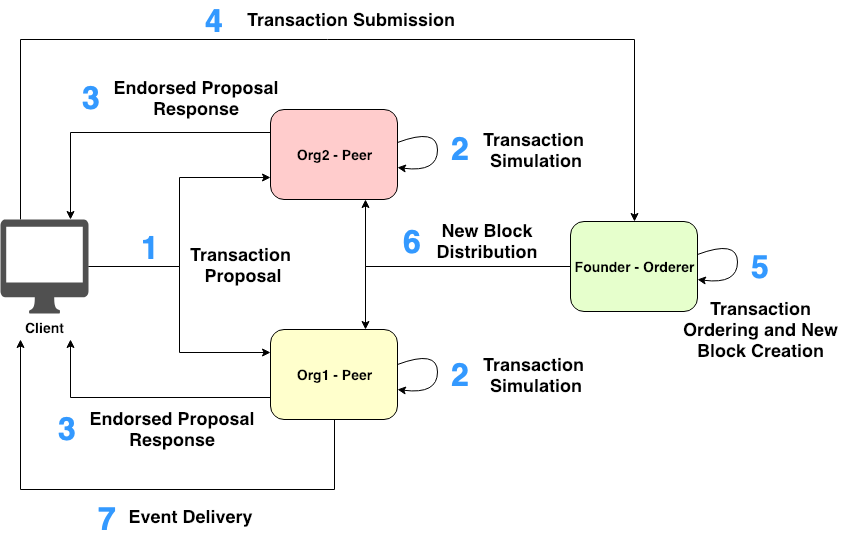
# Fabric transaction workflow:
- 1. Client:创建交易提议,并使用用户证书进行签名,然后发送交易到特定通道上预先确定的背书节点上
- 2. (Endorsing Peer) 首先从交易提议中验证用户身份和授权, 验证通过后,背书节点模拟交易, 生成相应和读写集,并使用证书对生成的响应进行背书
- 3. Client: accumulate并检查来自背书节点的背书提案响应.
- 4. Client: 将附有背书提案响应的交易发给Orderer.
- 5. Orderer: 对接收到的交易进行排序,生成一个新的有序交易快,并用其证书对生成的快进行签名
- 6. Orderer: 将生成的快广播给相关通道上的所有对等(endorse peer, commit peer)节点. 然后每个Peer确保接收到的区块中的每次交易都由适当的背书(Endorsing Peers)签名(根据调用的链码的背书策略确定)并且存在足够的背书. 之后,将进行版本检查(Multi-version concurrency control MVCC 检查) 以验证接收到的快的交易的正确性. 每一个Peer节点都会将每个交易的readset与其分类帐的世界状态进行比较,如果验证检查通过,则交易被标记为有效,并且每个Peer的word state都会更新, 否则,交易被标记为无效而不更新world state. 最后,无论该block是否包含任何无效的交易,接收到的block都会追加到Peer节点的本地blockchain中.
- 7. Client: 客户端从EventHub服务接受订阅的事件Fabric Orderer Service
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8> It acts as a Hub for distributing blocks of transactions to all peers on a relevant channel.
> Orderer might be considered to be the weakest point in the Fabric network.
# two type of Fabric Orderer service
- Solo-based ordering service (仅用于开发阶段)
- Kafka-based ordering service (搭建Kafka集群)
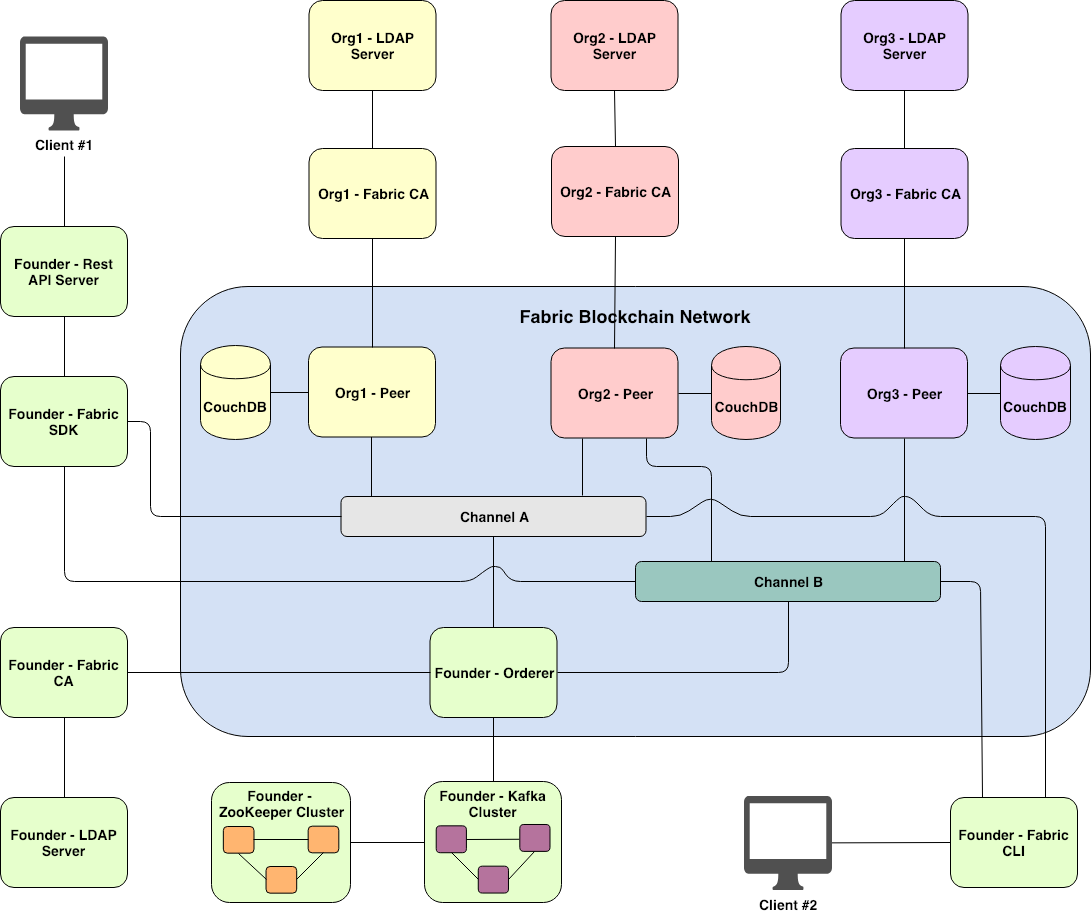
- Kafka provide Crash Fault tolerance (CFT崩溃容错) consensus(共识)Fabric network in a production environment
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22# Client application interact with Fabric blockchain network in two ways:
- Fabric SDK
> Fabric SDK supports Go, Node.js and Java language
- Fabric CLI
> use in development or maintenance mode
# CA: 用户管理和证书颁发
- Two ways to deploy Fabric CA:
- 1. Fabric CA without LDAP Server:
> Fabric CA 负责 用户注册、用户认证、颁发用户证书.
- 2. Fabric CA with LDAP Server:
> Fabric CA 负责颁发用户证书
> LDAP Server 负责 用户注册、用户认证、撤销用户
> 这种方式适合组织存在的AD,LDAP or Radius server.
# CouchDB:
> 支持JSON 查询,数据库索引,数据拷贝,ACID 属性
# LevelDB:
> 支持有限的操作
Private Data Collection
1 | Fabric 1.2支持该特性 |
Overview of Private Data Collection
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
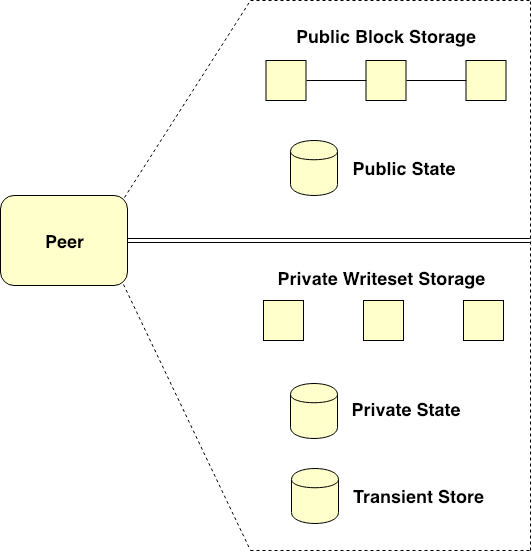
19# public data section:
- public block storage: 公共快存储
> is a blockchain that holds the history of all public transactions for every chaincode instantiated on a channel.
- public state database 公共状态数据库
> maintains the current state of public variables for a specific chaincode.
> 对于任何特定通道channel,即公共数据部分仅包含单个公共快存储(public block storage)实例, 但该部分可以包含基于在通道上实例化的多个链码(chaincode)的多个公共状态数据库实例.
# private data section:
- private writeset storage: 私有写入集存储
> 收集特定私有数据集合的所有私有交易的历史记录
> 这种存储不是区块链,而是一种典型的日志持久化数据库
- private state database:
>
- transient store database: 瞬态存储数据库
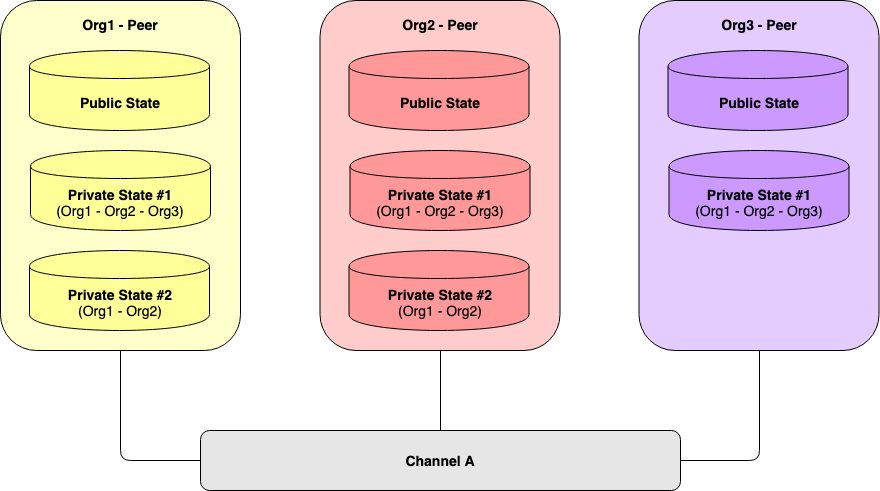
> 这种数据库用作临时数据库,用于在交易调用过程中临时存储私有数据Peers maintaining multiple Private Data Collections
1
2
3
4
5Public State Database:
(公共状态数据库)存储特定链码的公共变量的当前值, 还存储与该特定链码关联的修改后的私有数据集的哈希值.
Private data collections:
Fabric (1.4.12) 源代码分析
1 | # 下载docker镜像、预编译程序 |
Fabric Tips && Tracks
- Read-Write set semantics
1
专业术语:
transaction (交易):
chaincode的invoke或instantiate操作,invoke是从ledger中请求read-write set, instantiate是请求在peer上启动chaincode容器
system chain (系统链):
包含在系统级定义网络的配置区块中,系统链存在与ordering service中,与channel类似.
state database (stateDB):
current state数据存储在stateDB中,包括levelDB和couchDB.
proposal(提案):
一种对channel中某peer的背书请求,每个proposal要么是chaincode instantiate(实例),要么是chaincode invoke(调用).
policy(策略):
peer(节点):
网络实体,维护ledger并运行chaincode容器来对ledger执行read-write操作
ordering service(排序服务/共识服务):
将交易排序放入block的节点的集合,以先进先得的方式为网络上所有的channel提供交易排序服务.
membership services(成员服务):
在许可的区块链网络上认证、授权和管理身份. 在peer和order中运行的成员服务的代码都会认证和授权区块链操作, 他是基于PKI的MSP实现的.
fabric-ca 组件实现了成员服务以管理身份,处理ECert和TCert的颁发和撤销
ECert是长期的身份凭证,TCert是短期身份凭证membership service provider (MSP):
Member(成员):
Ledger (账本):
leading peer (主导节点):
每一个member在其订阅的channel上可以拥有多个peer, 其中一个peer会作为channel的leading peer代表该member与ordering service通信. ordering service将block传递给leading peer, 该peer再将block分发给同一member下的其他peer.
invoke (调用):
调用chaincode内的函数, invoke结构就是一个函数和一个参数数组.
instantiate (实例化):
启动chaincode容器的过程
gossip protocol (Gossip 协议):
Gossip 数据传输协议有三项功能: 管理peer discovery和channel 成员; 在channel上所有的peer间广播账本数据;在channel上所有的peer间同步账本数据
genesis block (初始化区块):
genesis block是初始化区块链网络或channel的配置区块,也是链上的第一个区块
fabric-ca:
默认的证书管理组件,向网络成员及其用户颁发基于PKI的证书,CA为每个成员颁发一个根证书(rootCert), 为每一个授权用户颁发一个注册证书(eCert), 每一个注册证书颁发大量交易证书(tCert)
endorser:
背书节点
dynamic membership (动态成员):
fabric 支持动态添加、移除members、peers和ordering服务节点, 而不会影响整个网络的操作性. 当业务系统调整或因各种原因需要添加、移除实体时.
consensus (共识):
用于产生一个对于排序的同意书和确认构成区块的交易集的正确性
concurrency control version check (并发控制版本检查):
CCVC时保持通道中各对等节点间状态同步的一种方式,对等节点并行的执行交易
committer:
提交者